- Company
- Press Center
- A Guide to NAND Flash: Maximizing Speed and Lifespan
BLOG
2023.02.15
A Guide to NAND Flash: Maximizing Speed and Lifespan
SHARE
NAND Flash is a type of non-volatile storage technology that is widely used in electronic devices such as USB drives, memory cards, and solid-state drives (SSDs). It has become increasingly popular over recent years for its fast read and write speeds, low power consumption, and durability. In this article, we'll take a brief look at the history of NAND Flash, explore the different types of NAND Flash, including SLC, MLC, TLC, and QLC, and introduce Cervoz's vast Flash offerings.
Temperature DRAM?
The first NAND Flash technology was developed in the late 1980s in Japan, and was named after the NAND gate, a type of digital logic gate. The technology was first used as a replacement for traditional EPROM and EEPROM memory, which required a special device to erase and rewrite data. NAND Flash differed because it could be easily rewritten and erased in blocks, rather than individually like with EPROM and EEPROM. This made it much faster and more efficient to use, and was the reason for its mass adoption over the following thirty years.
The Different Types of NAND Flash
There are several different types of NAND Flash, each with their own unique characteristics:
Single-Level Cell (SLC) NAND Flash stores one bit of data on each cell is the highest-performing type of NAND Flash available right now. SLC Flash has fast read and write speeds and a long lifespan, but it has a relatively low storage density compared to other types of NAND Flash, which makes using it quite expensive, especially for integrators with large storage needs.
Multi-Level Cell (MLC) NAND Flash stores two bits of data on each cell. Compared to SLC, it is slower, has a shorter lifespan, is less expensive and has more storage density.
Triple-Level Cell (TLC) NAND Flash stores three bits on each cell, and subsequently has even slower read and write speeds than SLC and MLC. However, due to its large data density, it is affordable and therefore commonly used in consumer devices such as USB thumb drives and memory cards.
Quad-Level Cell (QLC) NAND Flash stores four bits on each cell, unlike other types of Flash memory which store one, two or three bits per cell. It is designed to be even less expensive than Triple-Level Cell (TLC) NAND Flash, but it also has slower performance and a shorter lifespan.
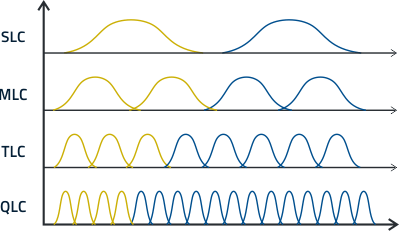
▪ SLC (single level cell) stores 1 bit per cell
▪ MLC (multiple level cell) stores 2 bits per cell
▪ TLC (triple level cell) stores 3 bits per cell
▪ QLC (quadruple level cell) stores 4 bits per cell
▪ MLC (multiple level cell) stores 2 bits per cell
▪ TLC (triple level cell) stores 3 bits per cell
▪ QLC (quadruple level cell) stores 4 bits per cell
How to Pick the Right NAND Flash for Your Application
When choosing the right NAND Flash for your application, you'll want to consider several factors. These include the required read and write speeds, the lifespan of the device, how much storage you need, and your budget. If speed and durability are most important to you, consider SLC NAND Flash; if cost is a major concern, TLC or QLC NAND Flash may be a better option.
Cervoz's Flash Offerings
Cervoz Industrial SSDs, featuring SATA interfaces and conforming to SATA III standards, are available in four series:, Titan (TLC), Momentum (MLC), Reliance (RO-MLC) and Supreme (SLC). Built to industrial grade specs, these SSDs employ the fixed BOM principle and long life-cycle management. Available in standard and wide temperature ranges, with multiple storage options, Cervoz's SSDs have been rigorously tested and verified for compatibility and reliability across various platforms.
Contact us to learn more about Cervoz products.

